Maximizing Campus Safety: A Comprehensive Guide To EMNS Compliance And The Value Of Unified Electronic, Indoor, And Outdoor Solutions
Picture this: it’s a tranquil morning on a bustling university campus. The sun is just beginning to peek over the horizon, casting a warm glow on the manicured lawns and stately buildings. Students shuffle sleepily to their classes, savoring the quietude of the early hours. Suddenly, the tranquility is shattered by a piercing siren, signaling an emergency on campus. Panic ensues as students and faculty scramble for safety, their hearts pounding with fear and uncertainty.
In the midst of chaos, university officials frantically attempt to activate the campus alert system, a critical lifeline in times of crisis. Yet, to their dismay, the system falters, its outdated infrastructure unable to handle the surge of alerts needed to inform and protect the campus community. As precious seconds tick by, the delay in communication proves costly, leaving students and staff vulnerable and exposed.
This harrowing scenario may seem like the plot of a suspenseful thriller, but for many educational institutions across the country, it’s a chilling reality. In today’s rapidly evolving threat landscape, the need for robust Emergency Management and Notification Systems (EMNS) has never been more urgent. Regulatory mandates such as the Clery Act, HEOA Act, Ray Baum Act, and Kari’s Law underscore the importance of proactive safety measures to safeguard campus populations from potential dangers.
As seasoned veterans in the field of emergency preparedness, we understand the gravity of the situation. That’s why we’re here to shed light on the intricacies of EMNS compliance and the transformative power of Unified Electronic, Indoor, and Outdoor solutions. Through a comprehensive analysis of a prominent university’s recent compliance shortcomings, we’ll uncover the critical role that cutting-edge technologies like SiSA: Critical Event Management Software play in fortifying campus safety protocols.
But before we dive into the details, let’s take a moment to reflect on the significance of this issue. The safety and well-being of our nation’s students, educators, and staff are non-negotiable priorities. Every individual has the right to feel secure in their learning and working environments, free from the specter of violence or harm. By confronting the challenges of EMNS compliance head-on, we can pave the way for a future where campuses are not only centers of academic excellence but bastions of safety and security.
With this goal in mind, let’s embark on a journey of exploration and discovery. Together, we’ll navigate the complexities of EMNS regulations, uncovering the hidden pitfalls and potential solutions along the way. Through real-world examples and expert insights, we’ll illuminate the path forward, empowering educational institutions to embrace innovation and resilience in the face of adversity.
So, dear reader, are you ready to join us on this transformative journey? Prepare to be inspired, informed, and empowered as we unravel the mysteries of EMNS compliance and chart a course toward a safer, more secure future for all. The adventure awaits – let’s embark on it together.

The Clery Act plays a crucial role in campus safety by requiring educational institutions to report campus crime statistics and security information. Its enactment was a response to the tragic death of Jeanne Clery, emphasizing the need for transparency and accountability in campus safety. This act has evolved over the years to include a wide range of crime reporting categories, ensuring students and staff are aware of the safety conditions on their campuses.
The Higher Education Opportunity Act (HEOA), building on the foundation laid by the Clery Act, introduced requirements that address a broader spectrum of safety and emergency preparedness concerns. It specifically targets the improvement of fire safety measures in student housing and mandates institutions to plan and implement emergency response procedures effectively. This act represents a holistic approach to campus safety, covering aspects from fire safety to emergency management plans, reflecting the understanding that preparedness is key to ensuring the welfare of the campus community.
Ray Baum’s Act and Kari’s Law focus on enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of emergency communication systems. They address critical issues in the infrastructure of communication systems that can hinder emergency responses. Ray Baum’s Act, for instance, ensures that emergency responders can locate the caller quickly, which is vital in campus environments where buildings and residences can be sprawling and complex. Kari’s Law, on the other hand, mandates direct and immediate access to emergency services without additional dialing requirements, which can save precious time during emergencies. These laws collectively underscore the importance of integrating advanced communication technologies with safety protocols to protect individuals in educational settings.

To address the compliance issues identified, educational institutions can implement several strategic solutions:

The evolution of Unified Electronic, Indoor, and Outdoor solutions is largely driven by advancements in technology, particularly in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). These technologies enable smarter, more responsive EMNS systems capable of analyzing vast amounts of data to identify potential threats and automate responses. For example, AI can enhance visual surveillance systems with facial recognition and abnormal behavior detection, allowing for immediate action even before human operators are aware of an issue.
A critical feature of Unified EMNS is the integration of various communication channels to ensure no one is left uninformed during an emergency. This integration encompasses traditional methods like sirens and PA announcements with modern technologies such as mobile apps, digital signage, and wearable devices. The goal is to reach every individual, regardless of their location on campus or the device they’re using, with consistent and clear messaging.


Unified EMNS solutions not only facilitate communication during emergencies but also enhance situational awareness for first responders and emergency management teams. By consolidating information from various sources—such as surveillance cameras, access control systems, and external data feeds—these systems provide a comprehensive overview of the situation as it unfolds. Enhanced situational awareness enables more informed decision-making, ensuring that response efforts are targeted and effective.
The adoption of Unified EMNS solutions represents a shift towards a more proactive and integrated approach to campus safety and emergency management. By leveraging cutting-edge technology and ensuring seamless communication across all platforms, educational institutions can not only comply with safety regulations but also foster a culture of preparedness and resilience. In the long term, this approach can transform how campuses respond to emergencies, making them safer places to learn, work, and live.
Unified EMNS solutions offer a comprehensive approach to campus safety, integrating cutting-edge technologies with diverse communication channels to ensure timely and effective emergency response. By adopting these solutions, educational institutions can enhance their preparedness for a wide range of potential threats, from natural disasters to security breaches. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities of EMNS systems, promising even greater advancements in campus safety and emergency management.

An often-overlooked aspect of Unified EMNS solutions is their potential to foster community engagement and safety education. Educational institutions can use these systems to conduct regular safety drills, disseminate educational materials on emergency preparedness, and engage with local emergency services for joint response exercises. This proactive approach to safety education ensures that the campus community is not only aware of the emergency protocols but also actively participates in maintaining a safe environment.

Unified EMNS solutions provide a unique opportunity to integrate emergency management practices directly into educational programs. By incorporating safety and emergency preparedness courses into the curriculum, institutions can equip students with critical life skills while also enhancing their understanding of the technology and strategies behind the EMNS.

Looking ahead, the future of campus safety and Unified EMNS solutions is poised for significant technological advancements. Innovations in IoT (Internet of Things) devices, autonomous response systems, and blockchain for secure communication are expected to further enhance the capabilities and reliability of EMNS. Additionally, the integration of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) in emergency training exercises could revolutionize the way institutions prepare for potential crises.

As educational institutions worldwide adopt Unified EMNS solutions, a global perspective on campus safety emerges. Collaborations between institutions across different countries can lead to the sharing of best practices, technological innovations, and joint initiatives aimed at enhancing safety standards globally. This international cooperation enriches the collective knowledge base, driving continuous improvement in campus safety technologies and strategies.

The discussion on Unified EMNS solutions in education, enriched with perspectives on community engagement, educational integration, future technological trends, and global cooperation, demonstrates the multifaceted value of these systems. As educational institutions continue to evolve and adapt to new challenges, Unified EMNS solutions stand at the forefront of ensuring campus safety and preparedness. By embracing these advanced technologies and strategies, campuses can not only meet current safety requirements but also anticipate and mitigate future risks, ensuring a secure learning environment for all.
SiSA is built on a robust technical foundation that leverages the latest in cloud computing, IoT (Internet of Things), and cybersecurity technologies. At its core, SiSA operates on a secure cloud-based platform, ensuring unparalleled reliability and scalability. This cloud infrastructure allows for real-time data processing and analytics, crucial for the immediate dissemination of alerts and information during emergencies.
The integration of IoT technology is a hallmark of SiSA’s approach to campus safety. By connecting various sensors and devices across a campus, SiSA can monitor environmental conditions, detect unauthorized access, and even identify signs of potential threats through anomaly detection algorithms. For instance, smoke detectors, door sensors, and CCTV cameras all feed into SiSA’s central system, providing a comprehensive overview of campus safety in real time.
In today’s digital age, the security of emergency management systems is paramount. SiSA employs state-of-the-art encryption protocols and cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and communications. Regular security audits and adherence to industry best practices ensure that SiSA remains impervious to cyber threats, safeguarding not only the system’s integrity but also the privacy and safety of the campus community.
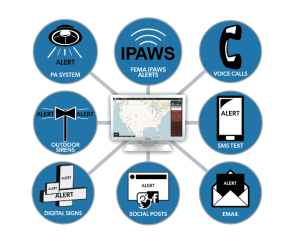
Delving deeper into the capabilities of SiSA, several advanced features stand out, making it a leader in the field of emergency management:
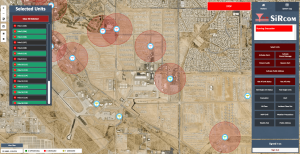
Imagine a sprawling university campus with diverse facilities, including residential halls, research labs, and lecture buildings. The university decides to implement SiSA as its unified emergency management solution. Shortly after deployment, a lab experiment goes awry, leading to a hazardous chemical spill.
Instantaneously, SiSA’s IoT sensors detect the chemical’s presence, triggering an automatic lockdown of the affected building. Alerts are sent out through various channels, including SMS, email, and digital signage, providing clear instructions on avoiding the area. Meanwhile, SiSA’s interface offers emergency responders a detailed layout of the lab, including access points and ventilation controls, facilitating a swift and effective response.
In the aftermath, SiSA’s reporting tools generate a comprehensive analysis of the incident, from the initial alert to the all-clear signal. This report is invaluable for reviewing response actions, identifying areas for improvement, and refining emergency protocols for future incidents.
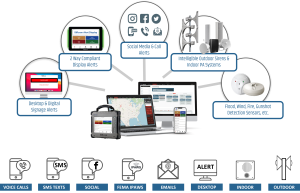
In reflecting upon the evolving landscape of campus safety, the journey through the intricacies of Unified EMNS solutions underscores their pivotal role in not just meeting regulatory requirements but in fundamentally enhancing the safety and well-being of educational communities. This exploration has illuminated how the integration of electronic, indoor, and outdoor solutions forms the backbone of a comprehensive emergency management strategy, capable of addressing the multifaceted nature of campus safety challenges.
Central to this new paradigm is SiSA, a beacon of innovation in Critical Event Management Software, embodying the full potential of Unified EMNS solutions. SiSA transcends traditional notification systems by offering a seamless, integrated platform that ensures timely and effective communication across the entire campus. Its sophisticated approach—merging predictive analytics, dynamic geofencing, and automated response protocols—equips educational institutions with the tools necessary for proactive risk management and emergency response.
As we conclude this exploration, it becomes clear that SiSA is not merely a technological solution but a catalyst for a broader transformation in how campus safety is conceived and implemented. By fostering a culture of preparedness, empowering communities with the knowledge and means to contribute to their safety, and leveraging state-of-the-art technology, SiSA charts a new course in campus safety management. It invites educational institutions to envision a future where safety is woven into the fabric of campus life, ensuring that learning environments are not only places of intellectual growth but also sanctuaries of safety and security.
In embracing SiSA and the comprehensive approach it represents, campuses can navigate the complexities of today’s safety challenges with confidence. As this blog comes to a close, let it be a call to action for educational institutions to prioritize the adoption of Unified EMNS solutions like SiSA, setting a new standard for campus safety in an ever-changing world.

HQE Systems is a certified Veteran Owned Company. For more information about HQE Systems Inc. and its emergency management, electronic security, and integration solutions, please visit www.hqesystems.com.

Contact: David Ditto (Early Warning Systems Subject Matter Expert)
Email: David.Ditto@hqesystems.com
Phone Number: (843) 872-7020
____________________
HQE Systems, Inc. | HQE is a Minority-Owned Service Disabled Veteran Owned Small Business (SDVOSB) providing full solutions for: Mass Notification Systems, Electronic Security Systems, Software Development Services, Contract Support, and Prototyping Services. As a brand-agnostic solutions provider, HQE prides itself in providing the BEST solution for the project. HQE possesses over 30+ factory certifications and reseller licenses to ensure our clients receive the highest quality service at the ideal budget. HQE can provide full design, installation, integrations, upgrades, and long-term maintenance support for any size and scope project.
